You might be surprised to learn that combination locks date back to ancient civilizations, where their early designs laid the groundwork for modern security systems. As you explore their evolution from basic mechanisms to the sophisticated models we use today, you’ll uncover how each advancement contributed to enhancing security. You’ll also find out what makes these locks tick—literally and figuratively—and why understanding their inner workings matters, especially in today’s context of rising security challenges. What innovations have shaped their current state, and what’s coming next?
Key Takeaways
- Combination locks originated from ancient Greek and Roman designs and evolved significantly in 19th-century England with intricate mechanisms.
- The first commercial combination lock was invented by Linus Yale Jr. in the 1860s, prioritizing security features.
- Key components of combination locks include a dialing mechanism, rotating discs, and a locking lever, which work together to release the bolt.
- There are various types of combination locks, including single-dial rotary locks, electronic locks, and dual-control systems, each suited for different applications.
- Modern advancements in lock technology include electronic and smart locks offering features like keyless entry, remote access, and enhanced security through biometrics.
Historical Overview of Combination Locks

Although combination locks may seem like a modern invention, their history dates back several centuries, showcasing an evolution in both design and security techniques. The ancient Greeks and Romans utilized rudimentary locking mechanisms that paved the way for contemporary systems.
By the 19th century, locksmiths in England began refining these devices, incorporating more intricate wheel mechanisms and rotating discs. The invention of the first commercial combination lock is attributed to Linus Yale Jr. in the 1860s, whose designs emphasized enhanced security features.
As the demand for reliable safekeeping arose, manufacturers like Sargent & Greenleaf popularized these locks. By incorporating mathematical principles and complex combinations, these advancements addressed vulnerabilities in traditional locking methods, ensuring the safety of valuable possessions and sensitive information.
Mechanisms Behind the Locks
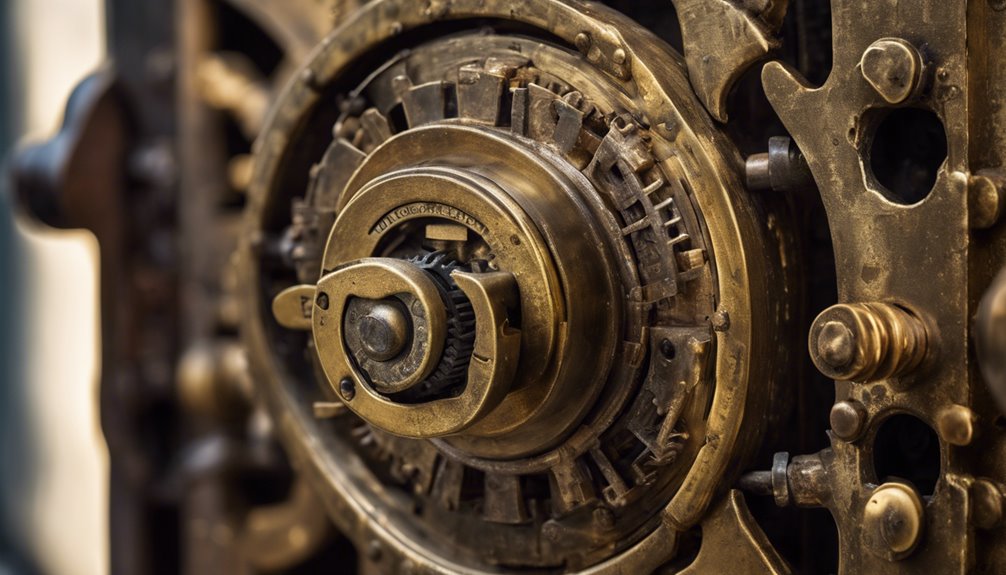
Combination locks operate through a series of mechanical interactions that transform your input into a secure alignment of internal components. When you dial a number, the rotating discs or gears respond to the specific sequence you enter. Each component engages with a notched lever, aligning with the bolt for release only when the correct combination is achieved. High-security locks often employ advanced mechanisms to offer enhanced protection against unauthorized access.
Historically, designs have evolved from simple cipher mechanisms to intricate systems employing multiple discs for heightened security. The precision of these mechanisms hinges on tolerances, ensuring minimal wear and maximum reliability. In addition, lock pins and tumblers can be found in many other locking systems, adding layers of security through their intricate design.
Your understanding of these interactions not only enhances security but also deepens appreciation of the engineering mastery behind these enduring devices. Mastering the mechanism is essential for anyone keen on locksmithing or security engineering.
Key Components of Combination Locks

Understanding the intricate mechanisms of combination locks leads to an appreciation of their key components.
At the core, you’ll find the dial or keypad, where user interaction occurs. The rotating cylinder connects to a series of cams and gears that translate your input into a specific release sequence.
Inside, there’s the disc assembly, often composed of a series of notched discs that align to a predetermined combination. Each notch interacts with a pawl or locking lever, which disengages only with the correct alignment.
The shackle serves as a physical barrier, securing the lock’s mechanism.
Historical innovations, like the introduction of the number wheel by Joseph Bramah in the 19th century, evolved this technology, enhancing security and user complexity.
Mastering these components grants deeper insight into both function and history.
Different Types of Combination Locks

When you explore different types of combination locks, you’ll find a range of mechanisms designed for various security needs.
From the traditional Group 1 locks to modern electronic keypad variants, these devices each offer unique features influenced by advancements in technology and historical design evolution.
Understanding the nuances of padlocks and their specific applications can greatly enhance your approach to securing personal and commercial spaces.
Group 1 Locks
While exploring the domain of Group 1 locks, it is essential to recognize the variety of combination locks available, each designed for specific applications and security needs. Group 1 locks typically include single-dial rotary models, electronic combination locks, and dual-control mechanisms. Understanding their distinctions is significant for effective security implementations.
| Type | Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Single-dial rotary lock | Mechanical, one-turn operation | Safes, vaults, doors |
| Electronic combination lock | Digital, keypad entry | Office buildings, homes |
| Dual-control mechanism | Requires two unique inputs | High-security facilities, labs |
Padlocks Overview
Moving from Group 1 locks, let’s explore padlocks, which serve as a versatile option within the combination lock category.
Historically, padlocks emerged in the late 19th century, evolving from simple mechanical designs to intricate models. You’ll encounter several types: the dial combination padlock, featuring a rotating disc mechanism, and the multi-wheel variant that allows for increased security through staggered numerical settings. Investing in high-quality locks can provide a significant advantage in long-term safety when compared to cheaper alternatives.
Each design serves specific applications, from securing gates to high-security facilities.
When mastering these locks, understanding the interplay of tumblers and internal mechanisms is essential, as minor adjustments can considerably alter security levels. Furthermore, you’ll appreciate the importance of construction materials in durability and resistance against tampering.
In today’s security landscape, the choice between traditional padlocks and keyless locks is crucial for meeting various security needs.
As you investigate deeper, the nuances of padlock design become increasingly apparent.
Electronic Keypad Variants
As technology has advanced, electronic keypad combination locks have become increasingly popular for their ease of use and enhanced security features. These devices often incorporate microcontrollers and digital circuitry, allowing you to input codes with precision. Variants include standalone models, which require no networking, and smart locks that connect via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi for remote access. Additionally, many digital keyless locks utilize advanced encryption techniques, further securing user access and data.
Techniques like anti-tamper mechanisms and rolling codes provide additional layers of security, thwarting traditional bypass methods. Moreover, the integration of advanced smart lock technology has further improved user convenience and access control. Historically, the shift from mechanical to electronic systems heralded a new era, driven by the need for more robust solutions against unauthorized access.
Understanding these intricacies empowers you to select the ideal lock based on your security requirements, combining convenience with technological advancement.
Security Features and Vulnerabilities

Although combination locks are often regarded as secure mechanisms for safeguarding valuables, they possess inherent vulnerabilities that can be exploited by knowledgeable individuals.
One common weakness is the reliance on limited numerical combinations, which can be discovered through techniques like “lock manipulation,” enabling skilled users to deduce the correct sequence via sound or feel. Additionally, the use of anti-pick pins in more advanced lock designs can significantly enhance their resistance to manipulation.
Historically, the introduction of certain lock designs, such as the rotary dial, exhibited susceptibility to brute-force attacks, particularly when inadequate round-count protections were integrated.
Furthermore, environments where wear can affect tumblers lead to unintentional ease in access. Additionally, a lack of high-security features in standard combination locks can further diminish their resistance to unauthorized access.
Consequently, while these locks serve their purpose, awareness of their limitations is essential for effectively securing your belongings against determined adversaries. Understanding these vulnerabilities allows for informed security strategies.
Advances in Lock Technology

You’ve seen how traditional combination locks evolved, but today, electronic lock innovations are reshaping security paradigms.
With features like user-set combinations and smart connectivity, these locks provide enhanced customization and remote access. Moreover, smart security systems can often be integrated with electronic locks to create a more cohesive security network.
Historical advancements in materials and technology intertwine, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in secure access solutions. Furthermore, many smart locks, such as the Aqara Smart Lock U100, integrate various access methods to improve convenience and security.
Electronic Lock Innovations
While the evolution of combination locks typically evokes images of mechanical simplicity, recent advances in electronic lock technology have transformed security systems into highly sophisticated tools.
The integration of microcontrollers and biometric sensors has revolutionized how you secure spaces. You’ll find electronic locks employing encrypted algorithms, enhancing resistance against physical tampering and electronic bypassing. Additionally, many electronic locks now utilize Bluetooth connectivity, which allows for seamless integration with smart home ecosystems and enhances user convenience.
Furthermore, the advent of power over Ethernet (PoE) simplifies installation and maintenance, reducing reliance on battery life. Historical innovations, like the shift from mechanical keypads to touchscreen interfaces, embody a change toward user-friendly security solutions. Additionally, smart locks offer enhanced security features that can further bolster protection against unauthorized access.
These innovations not only offer convenience but also align security imperatives with modern architectural designs, illustrating a confluence of form, function, and security in evolving lock technologies.
Smart Lock Features
As you explore the domain of smart locks, you’ll discover a plethora of features designed to enhance security and user experience.
These locks integrate advanced technology, merging reliability with convenience.
Consider these standout features that define modern smart locks:
- Keyless Entry: Utilize biometric scans or PIN codes, eliminating the need for traditional keys.
- Remote Access: Control your lock via smartphone apps, allowing you to grant access from anywhere.
- Activity Log: Monitor entry and exit events through detailed logs, providing insights into who entered or exited.
- Auto-Lock/Unlock: Automatically engage or disengage the lock when you approach or leave, ensuring consistent security.
Additionally, many smart locks offer AI-driven threat detection, enhancing security by analyzing user patterns to anticipate potential risks. These systems often integrate with smart home security systems, providing a comprehensive solution to protect your home.
These innovations not only reflect a shift from mechanical to digital but also embody the evolution of locking mechanisms to meet contemporary security demands.
User-Set Combinations
The introduction of user-set combinations has revolutionized locking systems, enhancing both security and personalization. By allowing you to define your own access codes, these mechanisms introduce a level of flexibility previously unattainable.
Historically, traditional locks relied on fixed codes, easily compromised through standard manipulation techniques. Modern user-set combination locks employ advanced tumblers and rotating disc systems, which not only make unauthorized access challenging but also enable users to change codes frequently, mitigating risks of code leakage.
Utilizing algorithms that detect repeated patterns, these locks further bolster security. This synergy of customization and technology not only reflects personal security needs but also embodies evolving standards in access management, making understanding user-set combinations essential for mastering contemporary locking systems. Additionally, modern locks like the Ardwolf A20 provide multiple access methods, illustrating the shift towards more versatile security solutions.
Modern Applications of Combination Locks

Combination locks have evolved considerably from their early uses, finding a wide array of applications in contemporary life. These mechanisms are integral in various sectors where security demands precision and reliability. You encounter them in:
- Residential Security: Safeguarding homes against intrusions.
- Bicycles and Recreational Equipment: Offering protection against theft during outdoor activities.
- Safe Deposit Boxes: Ensuring that only authorized personnel can access valuable items.
- Gym Lockers: Providing users with a convenient yet secure storage solution.
Their design harnesses mechanical simplicity, often relying on disks, wheels, or electronic circuits, while still demanding your mental agility to recall combinations.
This historical evolution reflects an enduring commitment to safety and user empowerment in an ever-changing technological landscape. Understanding these applications enhances your mastery of combination security systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do I Reset the Combination on My Lock?
To reset the combination on your lock, locate the reset mechanism, often a small lever or button.
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for opening the current combination, then engage the reset feature.
Input your desired new combination, ensuring you remember each digit’s position.
Check the mechanism’s functionality by locking and opening with the new combination.
Finally, document the new combination securely for future reference, avoiding potential lockouts.
Can Combination Locks Be Picked Like Traditional Locks?
You might think picking a combination lock is as easy as pie, but it’s a different beast.
Unlike traditional pin tumbler locks, combination locks rely on specific rotations to align internal wheels.
While some expert lock pickers can manipulate them, it’s considerably more complex due to the rotational mechanism.
The challenge lies in accuracy and timing, making these locks tougher to bypass than you’d expect, ensuring better security for your belongings.
What Materials Are Used in Modern Combination Locks?
Modern combination locks typically utilize a blend of materials for durability and security.
You’ll find hardened steel used in the locking mechanism to resist tampering. Zinc alloys form the body for lightweight strength, while polycarbonate or ABS plastic often makes up the dial and casing, providing weather resistance.
The internal gears might incorporate brass for smooth operation.
These materials collectively enhance security, making contemporary locks more resistant to picking and brute-force attacks.
Are Combination Locks Weather-Resistant?
Combination locks are designed with varying levels of weather resistance, but did you know that about 70% of durable models feature weatherproof materials?
This capability often hinges on the construction, with polycarbonate and stainless steel prevalent in modern designs.
Historical advancements in gasket technology greatly enhance resistance to moisture and corrosion.
As a result, while no lock is entirely impervious, selecting quality models guarantees they withstand the elements better over time, preserving functionality and security.
How Long Do Combination Locks Typically Last?
Combination locks typically last anywhere from 5 to 20 years, depending on their materials and usage frequency.
If you opt for a high-quality lock made with durable materials, you can extend its lifespan considerably.
Regular maintenance, like lubricating mechanisms and avoiding exposure to harsh environments, can also enhance longevity.
Knowing when to replace your lock is essential; signs of wear may indicate it’s time for an upgrade to guarantee security remains tight.
Conclusion
As you navigate the labyrinth of locks throughout history, combination locks become the steadfast guardians of security, their intricate mechanisms akin to a well-tuned orchestra. Each component harmonizes, responding to your carefully crafted sequence like a maestro conducting a timeless symphony. In this evolving age, their metamorphosis mirrors society’s ever-advanced dance with technology. Just as ancient mariners relied on stars for navigation, you can trust in these locks to safeguard your treasures, bridging past ingenuity with present innovation.






