Discover the enthralling world of medieval locksmithing, where craftsmen intricately designed locks to protect coveted treasures and royal possessions. Their techniques involved precise key making processes that required patience and skill, alongside advanced lock picking methods like lever manipulation and impressioning. Essential tools such as key cutters and tension wrenches were utilized to craft intricate mechanisms that guarded against unauthorized access. Explore the evolution of lock designs and the security features implemented, showcasing the artistry and ingenuity of medieval locksmiths. The mysteries behind castle security and guild traditions await your discovery in this enchanting journey through history.
Key Takeaways
- Medieval locksmithing techniques included intricate key making and lock picking methods.
- Tools like tension wrenches and lock pick sets were essential for manipulating locks.
- Guilds and apprenticeships fostered innovation and quality standards in locksmithing.
- Lock mechanisms featured complex designs with false notches and spring-loaded pins.
- Key shapes varied for unique locks, requiring precise crafting and testing for functionality.
History of Locksmithing

During the medieval period, locksmithing emerged as an indispensable craft that played a significant role in safeguarding valuable possessions and securing properties. Techniques employed in this trade evolved alongside advancements in metallurgy and design, leading to the creation of more sophisticated locking mechanisms.
Medieval locksmith techniques were vital in developing intricate locks that required specialized knowledge to create and gain access to. Locksmiths of this era crafted locks using iron and bronze, fashioning them into intricate designs with multiple moving parts to enhance security, showcasing their mastery of historical locksmithing practices.
These skilled craftsmen utilized tools such as picks, tension wrenches, and key extractors to manipulate these complex locks. Locksmiths would meticulously shape keys by hand to fit the unique mechanisms of each lock they created. The keys were often ornately designed to reflect the status of the owner and to deter unauthorized duplication.
In medieval times, locksmiths were highly respected for their ability to safeguard important documents, treasures, and properties. Their expertise in designing and crafting secure locks guaranteed that only those with the proper knowledge and tools could gain access to protected areas.
Ancient Lock Designs

Let's take a look at the intriguing world of ancient lock designs.
Keyhole shapes varied widely, ranging from simple circles to intricate geometric patterns.
Understanding the top techniques used to manipulate these locks reveals the mechanical ingenuity and craftsmanship that went into their creation.
Mechanical mechanisms and security features in these ancient locks offer insights into the ingenuity of our ancestors.
Keyhole Shapes
Keyhole shapes in ancient lock designs varied greatly, reflecting the creativity and ingenuity of medieval locksmiths.
These unique keyhole shapes served not only as a security measure but also as a display of craftsmanship.
Here are some keyhole shapes commonly found in medieval lock mechanisms:
- Round: Circular keyholes were prevalent in simpler lock designs, requiring a round key to operate.
- Oval: Locks with oval keyholes provided a bit more complexity and were often used in more intricate mechanisms.
- Square: Square keyholes were a common choice for locks that required additional security measures.
- Irregular: Some medieval locksmiths crafted keyholes in irregular shapes to add an extra layer of complexity and challenge to lockpickers.
- Heart-shaped: A whimsical and rare design choice, heart-shaped keyholes were reserved for special or decorative locks.
Each keyhole shape not only had a practical function but also showcased the skill and artistry of the locksmiths of the time.
Mechanical Mechanisms
How did medieval locksmiths create intricate and secure mechanical mechanisms in their ancient lock designs?
Medieval locksmiths utilized a variety of tools and techniques to craft these sophisticated mechanical mechanisms. One key tool they relied on was the file, which allowed them to shape metal components with precision. By carefully filing down parts such as springs and levers, locksmiths could guarantee that the lock would function smoothly and reliably.
Additionally, medieval locksmiths made extensive use of the hammer and anvil to forge sturdy metal components for their locks. By hammering heated metal into shape on the anvil, locksmiths could create robust bolts and intricate key mechanisms that formed the backbone of their secure locks.
Furthermore, locksmiths often employed the drill to create small holes and intricate patterns in the metal components of the lock. This attention to detail not only enhanced the aesthetic appeal of the lock but also contributed to its security by making it more difficult to tamper with.
Security Features
Security was paramount in ancient lock designs, with medieval locksmiths implementing a variety of innovative features to safeguard their creations.
These medieval security measures included:
- Warded Locks: Utilized intricate internal wards that only allowed specially shaped keys to operate the lock.
- False Notches: Inserted to mislead potential lock-pickers, making it harder to decode the correct key pattern.
- Spring-Loaded Pins: Placed within the lock mechanism to add an extra layer of complexity and prevent unauthorized access.
- Master Key Systems: Enabled multiple locks to be opened with a single master key, offering convenience without compromising security.
- Complex Key Shapes: Designed with intricate patterns and varying depths to create unique combinations for each lock, enhancing security against manipulation.
Key Making Process

Crafting keys during the medieval period was a meticulous process that demanded skill and precision.
Key making was an essential aspect of medieval lock making, requiring locksmiths to carefully study the intricacies of each lock to create a precise key that could manipulate its mechanism. As the evolution of lock mechanisms progressed, locksmiths employed increasingly sophisticated techniques, mirroring the advancements seen in the historical evolution of lock mechanisms.
To begin, locksmiths would examine the lock to understand its unique configuration of pins and tumblers. Using this knowledge, they'd then select a blank key that closely matched the desired shape.
With the blank key in hand, the locksmith would meticulously file down its edges and grooves, gradually shaping it to align perfectly with the internal components of the lock. This process required patience and expertise, as even the slightest deviation could render the key ineffective.
Once the key was crafted to perfection, locksmiths would test it repeatedly in the lock to guarantee smooth operation. Through this methodical approach, medieval locksmiths were able to produce keys that could securely release the mysteries of medieval locks.
Lock Picking Techniques

Lock picking techniques were a clandestine art mastered by skilled individuals during the medieval era. In a time where security was of utmost importance, those with the ability to pick locks held a powerful skill set.
Many of the principles used in medieval lock picking laid the groundwork for modern methods, such as those found in mastering advanced lock picking techniques. Here are some medieval lockpicking techniques that were used:
- Raking: A technique where a pick with multiple peaks is inserted into the lock and jiggled up and down to set the pins quickly.
- Single Pin Picking: Involves manipulating each pin in the lock individually until all are set in the correct position.
- Tension Wrench: Applying the right amount of pressure to turn the lock while picking the pins.
- Lever Lock Manipulation: Used for lever locks, this technique involves lifting and holding the lock's levers in place to open it.
- Impressioning: Creating a working key by making a mold of the lock through trial and error.
These techniques required patience, precision, and a deep understanding of how locks functioned, making skilled lock pickers highly sought after during the medieval period.
Locksmithing Tools Overview
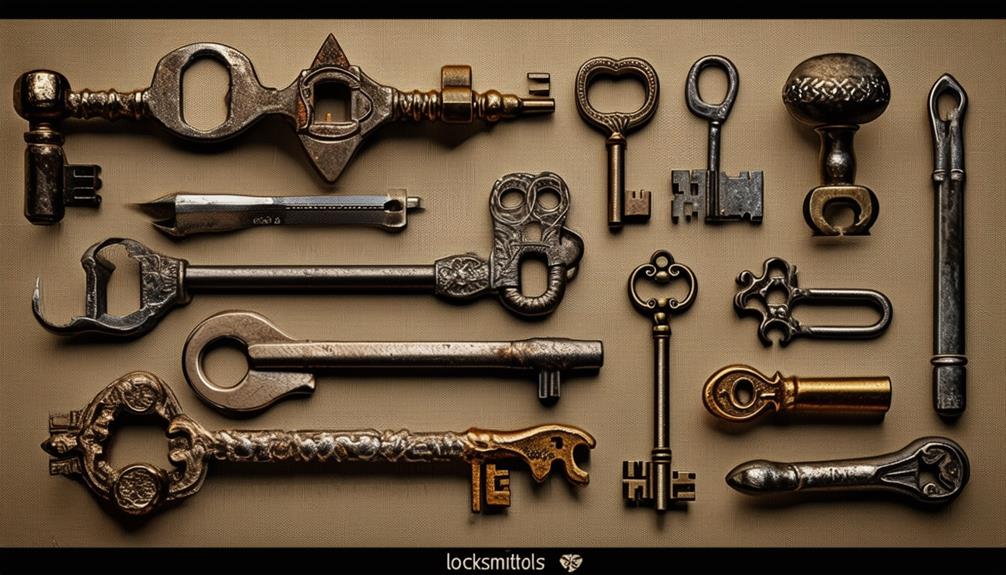

Let's talk about the essential locksmithing tools that were vital for medieval locksmiths.
These tools, often crafted with precision and care, included a variety of picks, tension wrenches, and specialized hammers that allowed locksmiths to manipulate locks effectively.
Discover the historical tool innovations that revolutionized the craft of locksmithing during this era, including tools of medieval locksmiths that were designed for both security and artistry.
Understanding these tools will provide insight into the intricate techniques used to create and manipulate locks in medieval times.
Essential Locksmithing Tools
Equipped with a diverse array of specialized tools, a skilled locksmith possesses the means to tackle a variety of lock-related challenges efficiently and effectively.
In medieval times, locksmiths relied on a set of essential tools to craft and manipulate locks with precision. These tools included:
- *Key Cutter*: A key cutter was used to shape keys accurately according to the unique configurations of locks.
- *Tension Wrench*: This tool applied pressure to the lock's cylinder to hold pins in place during picking.
- *Lock Pick Set*: Consisting of various picks and rakes, this set allowed locksmiths to manipulate the internal components of locks.
- *Plug Spinner*: The plug spinner was essential for quickly rotating the lock's plug after successfully picking it.
- *Impressioning Tools*: These tools enabled locksmiths to create a key by making impressions of the lock's pins.
With these essential tools in hand, medieval locksmiths honed their craft and opened the mysteries of intricate locks with skill and precision.
Historical Tool Innovations
Throughout history, locksmiths have constantly innovated their tools to meet the evolving demands of security and craftsmanship. The development of historic locksmith tools showcases the ingenuity and skill of locksmiths throughout the ages.
One significant innovation was the creation of warding tools, used to manipulate the internal mechanisms of locks by fitting into the wards within the keyway. These tools allowed locksmiths to create and repair intricate lock systems with precision.
Another essential advancement was the introduction of skeleton keys, versatile tools that could bypass a variety of locks by mimicking the shape of different key bits. This innovation revolutionized the locksmithing trade, making it easier to open various locks efficiently.
Furthermore, the creation of lever lock picks enabled locksmiths to manipulate the levers within lever tumbler locks effectively. These picks allowed for the precise lifting of individual levers, granting access to locked spaces.
Lever Lock Mechanisms
Medieval locksmiths revolutionized security with lever lock mechanisms, a sophisticated system that employed varying lengths of levers to control the locking and releasing of doors.
These locks weren't only advanced for their time but also demonstrated craftsmanship that would influence future designs, much like the design complexity of disc tumbler locks.
Lever lock mechanisms were a significant advancement in security during medieval times. Here's what you need to know about them:
- Lever Arrangement: Levers were arranged in a way that required them to be lifted to specific heights to align with the bolt, allowing the lock to open.
- Key Design: Keys had notches of different depths corresponding to the lever heights, allowing the key to lift the levers to the correct positions.
- Complexity: Lever locks could have multiple levers, increasing the complexity of the system and making it harder to pick.
- Security Features: Some lever locks had false notches or levers to deceive lockpickers.
- Variations: Lever locks came in various sizes and designs, catering to different security needs and door types.
Understanding the intricate workings of lever lock mechanisms sheds light on the craftsmanship and innovation of medieval locksmiths.
Pin Tumbler Locks

With the advent of pin tumbler locks, locksmithing in history took another leap forward. Pin tumbler locks are widely used today and have a simple yet effective design.
In these locks, a series of pins of varying lengths are housed within the lock cylinder. Each pin consists of a top and bottom segment. When the correct key is inserted into the lock, it lifts the pins to align perfectly along what's known as the shear line. This alignment allows the lock to turn, opening the mechanism.
Pin tumbler locks are considered secure due to their design complexity, as they offer effective against casual unauthorized access with intricate pin and key mechanisms that require precise alignment for releasing.
These locks are versatile and can be found in various applications, from household doors to high-security installations. Understanding the inner workings of pin tumbler locks can provide insight into how to better secure your belongings.
Master Key Systems

Let's talk about Master Key Systems, specifically Keyed Alike Systems, and Grand Master Keys.
These systems allow for multiple locks to be opened by the same key or a higher-level master key, providing convenience and efficiency in accessing various areas or buildings.
Master keying improves security by reducing the number of keys required for multiple access points, allowing authorized personnel seamless entry.
Keyed Alike Systems simplify key management, while Grand Master Keys grant access to all locks within a designated system.
Keyed Alike Systems
Keyed alike systems, also known as master key systems, are a practical method for simplifying access control in various settings. These systems offer a convenient solution for managing multiple locks efficiently.
Here are some key points to help you understand keyed alike systems better:
- Versatility: Keyed alike systems allow one key to open multiple locks, providing convenience and streamlining access.
- Control: They offer control over who can access specific areas while allowing authorized individuals to use a single key for various locks.
- Efficiency: This system reduces the number of keys needed, simplifying key management and enhancing security protocols.
- Customization: Keyed alike systems can be tailored to fit the unique needs of different environments, from residential buildings to commercial spaces.
- Security: Despite the convenience they offer, keyed alike systems maintain security levels by ensuring only authorized personnel can access designated areas.
Grand Master Keys
To understand the concept of Grand Master Keys, it's essential to explore the intricate world of master key systems.
Grand master keys are the highest level of access in a master key system. These keys are designed to open all locks within a specific set of keyed alike systems, offering unparalleled convenience and control.
In a master key system, various individual keys can operate specific locks, while a master key can open all locks within its group. A grand master key takes this concept further by providing access to multiple groups of locks, each controlled by its own master key.
This hierarchical structure allows for streamlined access management in large buildings or facilities.
Grand master keys are meticulously designed to guarantee security and functionality. Locksmiths carefully plan and craft these keys to maintain the integrity of the system while granting authorized individuals the necessary access.
Understanding the role of grand master keys in master key systems illuminates the sophisticated strategies employed in medieval locksmithing to safeguard valuable assets.
Locksmith Guilds & Apprentices

Exploring the world of medieval locksmithing reveals the integral role played by locksmith guilds and apprentices in shaping the craft.
These guilds not only facilitated the exchange of knowledge but also guaranteed that innovations in lock design, such as the evolution of lock picking techniques, were preserved and disseminated among members.
- Apprenticeships: Young individuals interested in becoming locksmiths would often start as apprentices under the guidance of skilled masters in medieval locksmith guilds.
- Training: Apprentices would receive hands-on training in crafting locks, creating keys, and understanding the intricate mechanisms involved in lock-making.
- Guild Regulations: Medieval locksmith guilds established strict regulations to maintain quality standards and protect the secrets of the trade.
- Journeyman Status: After completing their apprenticeships, locksmiths would attain journeyman status, showcasing their proficiency in the craft.
- Master Locksmiths: Masters were highly skilled locksmiths who'd proven their expertise and were tasked with passing down knowledge to apprentices, guaranteeing the continuity of the craft.
Joining a medieval locksmith guild as an apprentice was a prestigious path towards mastering the art of lock-making and securing valuable knowledge for future generations.
Securing Castles & Treasures

Securing castles and treasures in medieval times required sophisticated lock mechanisms crafted by skilled locksmiths. These locks were designed to protect valuable assets and keep intruders at bay.
One of the most intriguing aspects of securing castles and treasures was the medieval lockpicking secrets employed by locksmiths. Throughout history, locksmiths developed various intricate lock designs that not only served practical purposes but also showcased their artistry and ingenuity.
Locksmiths in medieval times used a variety of techniques to create intricate locks that were difficult to pick. They crafted these locks with precision and often incorporated hidden mechanisms to deter unauthorized access.
Locksmiths understood the importance of safeguarding castles and treasures, and their expertise was vital in maintaining security.
Medieval lockpicking secrets were closely guarded by locksmith guilds, passed down from master to apprentice. These secrets included knowledge of how different types of locks functioned and how to manipulate them effectively.
Locksmiths who mastered these techniques were in high demand, especially by nobles and royalty seeking to protect their riches.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Did Medieval Locksmiths Protect Their Trade Secrets?
To safeguard their trade secrets, medieval locksmiths employed various methods. They utilized intricate designs and mechanisms, limiting access to their workshops.
Locksmiths also relied on apprenticeships for passing down techniques orally from master to apprentice, ensuring knowledge stayed within the craft.
Additionally, guilds established strict codes of conduct and penalties for those who disclosed confidential information.
Through these practices, medieval locksmiths protected their valuable trade secrets from falling into the wrong hands.
Were Locksmiths Considered Skilled Artisans in Medieval Times?
Absolutely, in medieval times, locksmiths were indeed esteemed as skilled artisans.
Their meticulous craftsmanship and intricate designs set them apart as masters of their craft.
Locksmiths honed their skills through years of practice, blending creativity with precision to create secure and innovative locks.
Their reputation for excellence was well-deserved, earning them respect and recognition among their peers and the community at large.
What Materials Were Commonly Used to Make Medieval Locks?
In medieval times, locks were typically crafted from materials like iron, brass, and bronze.
These metals were commonly used due to their durability and malleability, allowing locksmiths to create intricate designs while ensuring security.
Iron, being strong and abundant, was a popular choice for creating sturdy lock components.
Brass and bronze were favored for their resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for locks that needed to withstand the test of time.
Did Medieval Locksmiths Face Any Competition From Other Trades?
Oh, medieval locksmiths were like knights battling for the key to success in a castle of trades!
They faced competition from metalworkers, blacksmiths, and carpenters, each vying for the kingdom's riches.
But with their intricate skills in crafting locks, locksmiths held the power to secure treasures and secrets.
Their expertise in manipulating metal and creating intricate mechanisms set them apart in the domain of tradesmen.
How Were Locksmithing Techniques Passed Down Through Generations in Medieval Times?
Locksmithing techniques in medieval times were passed down through generations by master locksmiths teaching apprentices.
You see, these skilled craftsmen shared their knowledge and expertise directly, ensuring the secrets of the trade were preserved and refined over time.
Conclusion
As you explore the world of medieval locksmithing, you uncover the secrets of the past and discover the intricate techniques and tools used to secure castles and treasures. Just like a key turning in a lock, each piece of knowledge you gain opens up a new domain of understanding. Keep investigating and you'll find yourself immersed in the fascinating history of locksmithing, where every detail holds a hidden treasure waiting to be revealed.









